3 Minute Read
It’s one of the trending topics right now in artificial intelligence, but there's a lot more than meets the eye when it comes to determining the main differences between AI and Responsible AI.
Simply put, AI technologies can either be designed, developed and implemented responsibly with safeguards in place to protect individuals and organizations or not.
Let's discuss what responsible AI means in a bit more detail.
Responsible AI is still an emerging area which predominantly focuses on AI governance. The use of the word responsible is an umbrella term that covers ethics, sustainable practices and democratization.
The following terms including; Responsible AI, Ethical AI and Trustworthy AI all relate to the principles behind the development, design and implementation of AI systems and platforms in a way that will benefit each individual, our society and businesses while reinforcing human centricity and societal value.
The term ‘Responsible’ still remains the most inclusive term ensuring that AI and machine learning systems are not just safe or trusted but respect and uphold human rights and societal values as well.
The main principles of Responsible AI include:
- Privacy-enhanced: Privacy is meant to enforce practices that help protect end-user autonomy, identity and dignity. Responsible AI technologies must be developed with values such as anonymity, confidentiality and control.
- Secure and resilient: Responsible AI systems should be built to avoid, protect against and respond to attacks, while also being able to recover from an attack.
- Safety First: Responsible AI shouldn't endanger human life, property or the environment.
- Fair & Reasonable without harmful or discriminative bias. Fairness is meant to address issues concerning AI bias and discrimination. This principle focuses on providing equality, equity and justice.
- Explainable and interpretable: Explainability and interpretability are meant to provide more in-depth insights into the functionality and trustworthiness of AI systems. Explainable AI, for example, is meant to provide users with an explanation as to why and how it got to its output.
- Accountable and transparent: Increased transparency is meant to provide increased trust in AI systems, while making it easier to fix problems associated with AI model outputs. This also enables developers more accountability over their AI systems.
- Valid and reliable. Responsible AI systems should be able to maintain their performance in different unexpected circumstances without failure.
What is AI Governance?
AI governance is the legal framework for ensuring AI and machine learning technologies are researched and developed with the goal of helping humanity navigate the adoption and use of these systems in ethical and responsible ways. AI governance aims to close the gap that exists between accountability and ethics in technological advancement.
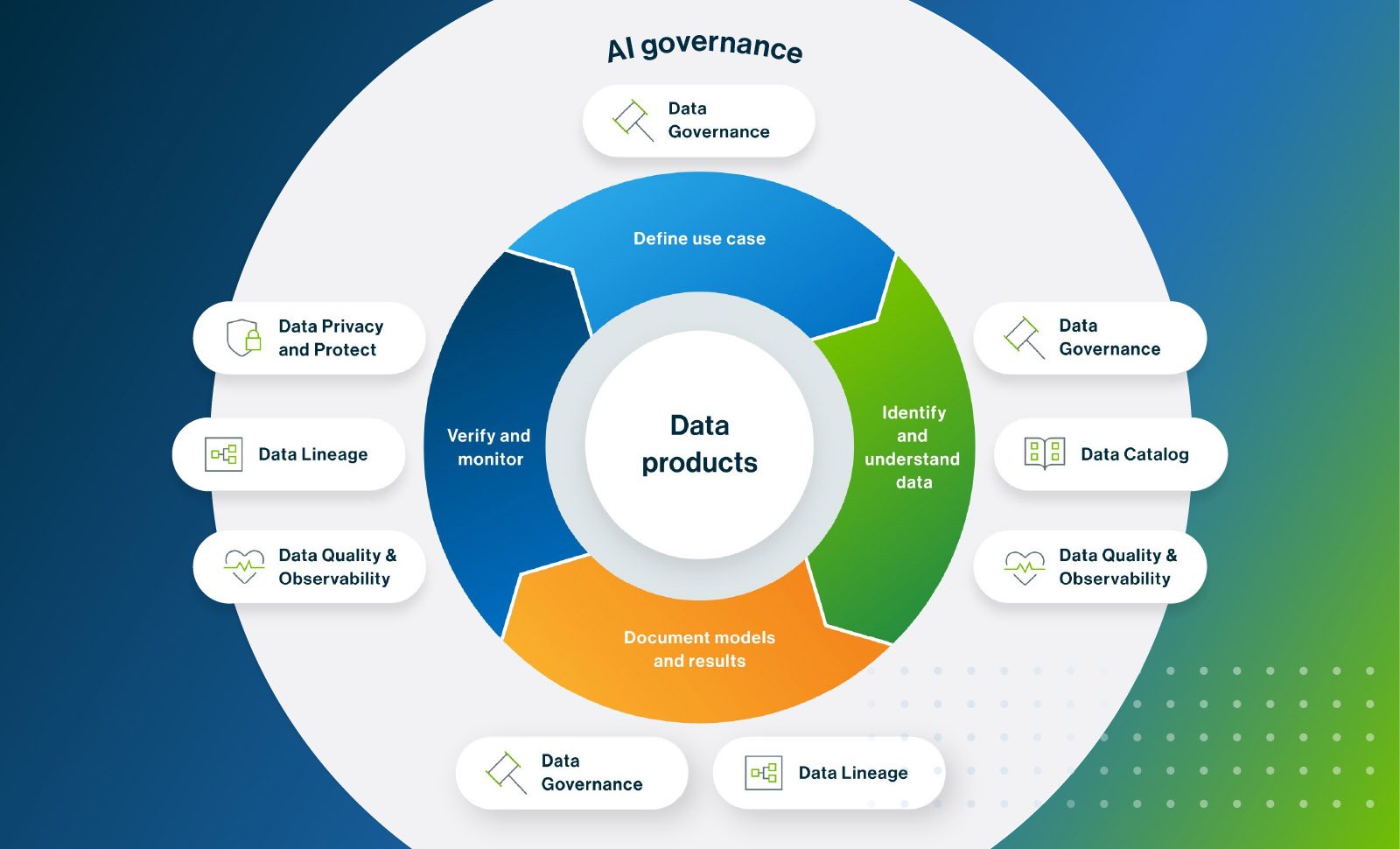 An example of an AI Governance framework by Collibra
An example of an AI Governance framework by Collibra
Some of the main areas of AI governance include:
- Assessing the safety of AI related to justice, data quality and autonomy
- Qualifying how daily life is shaped by algorithms and who controls monitoring it
- Determining which sectors are appropriate for AI automation
- Establishing legal and institutional structures around AI use and technology
- Defining the rules around control and access to personal data
- Dealing with moral and ethical questions related to AI
The implementation of responsible AI can help reduce AI bias, create more transparent AI systems and increase end-user trust in those systems. It's imperative that we minimize the harm done by AI and all contribute to help shape the future of AI so that humanity is protected and people retain their dignity and human rights.
Everyone has the right, responsibility and opportunity to help shape the future of AI for good and contribute to participating in global regulatory efforts and organizations working towards responsible AI practices.
For more information on how you can build a responsible AI framework for your brand or project, talk to us today.

